Knee arthritis
Knee replacement
WHAT IS ARTHRITIS?
Commonest cause of knee pain in old age is simple degeneration (wear and tear). This is known as osteoarthritis. About 18% of people in England over age of 45 have sought help for knee arthritis. That is almost one in five!
Other conditions such as inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid, psoriasis), severe knee injuries (prior ligament injuries) and removal of cartilage (menisectomy) can also cause knee arthritis.
HOW DOES IT PRESENT?
Knee arthritis causes pain, swelling, stiffness and reduced movements. You may notice pain around the kneecap and on inside of the knee with some pain in the back of knee. It is a dull ache especially on weight bearing. You may have a reduced walking distance and pain at night. You may find it difficult to straighten the knee or bend it fully.
HOW IS IT DIAGNOSED?
I find that in most cases your history and examination is sufficient to reach diagnosis. I will check your gait (walking pattern), hip, knee swelling and movements.
I will arrange x-ray of your knee to confirm any degenerative changes. Occasionally hip pain can cause referred pain in the knee, hence I will check your hips as well.
Early arthritis
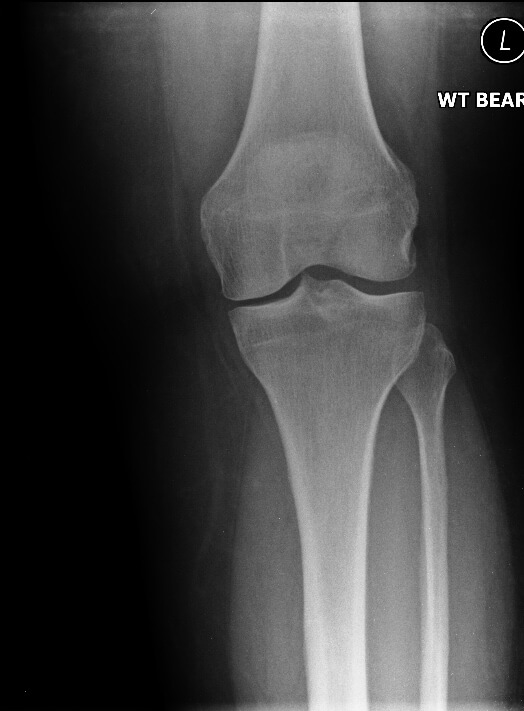
Moderate arthritis
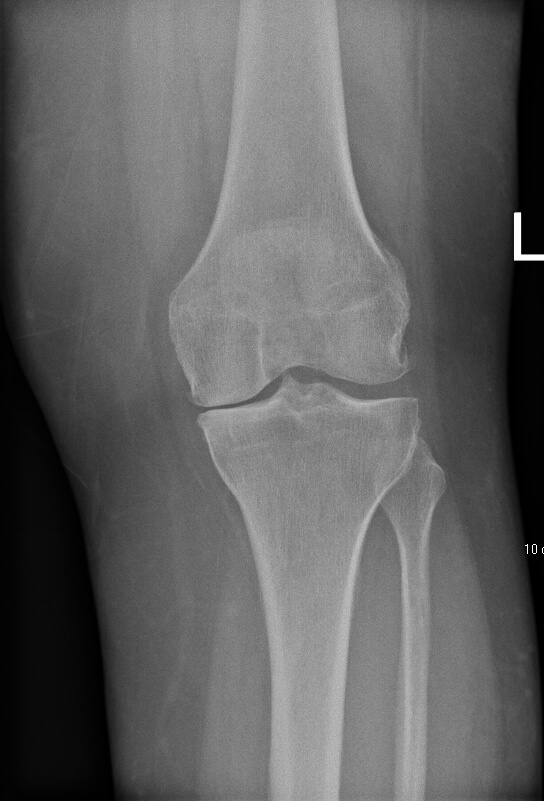
Severe arthritis
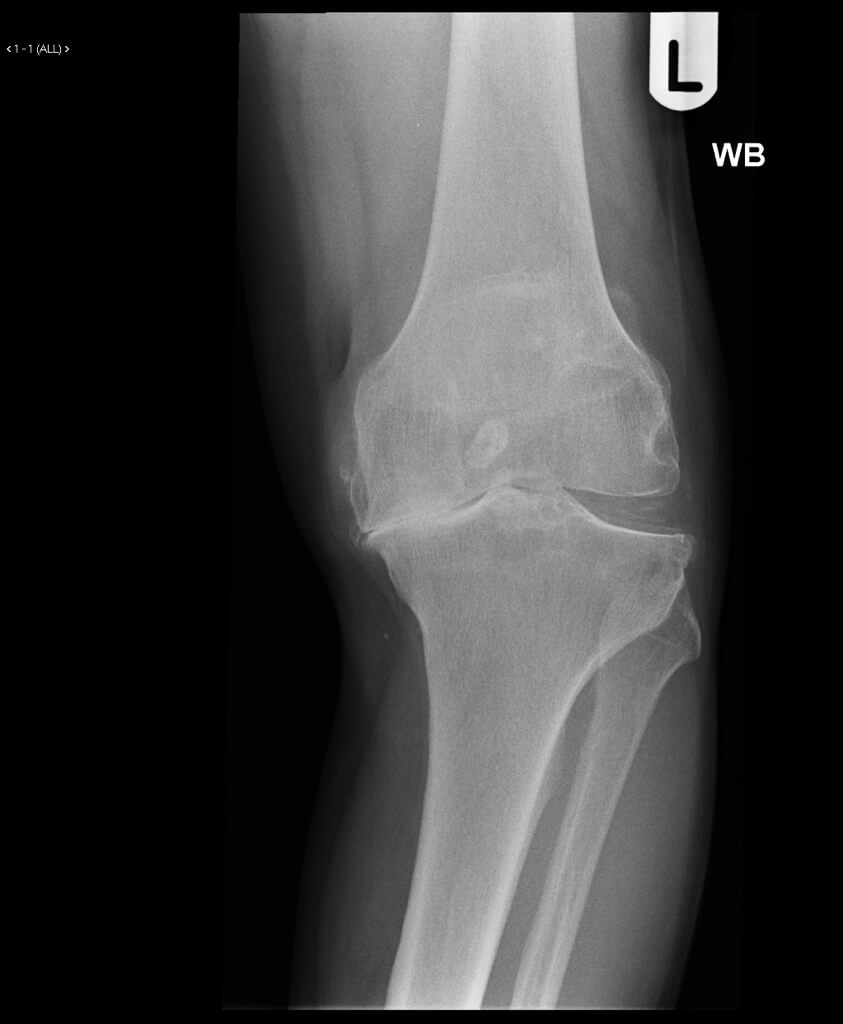
WHAT DOES THE OPERATION INVOLVE?
I perform the operation under spinal anaesthetic (needle in the back to freeze legs) or rarely under general anaesthetic.
I make a cut down the front of knee. I expose the worn joint and remove damaged part of knee. I then prepare end of thigh bone (femur) and top of shin bone (tibia) with saw and cutting guides. I then implant artificial joint using bone cement. After making last checks and wash, I close the wound.
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT?
Treatment of early arthritis initially includes:
- Pain killers, anti-inflammatory gel or tablet
- Weight loss
- Walking aid
- Physiotherapy (range of motion, aerobic and strengthening exercises)
- Intra articular steroid injection
WHAT ARE THE RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS?
Knee replacement has become a standard orthopaedic operation with excellent results.
It is extremely good at relieving arthritic pain. It has some risks and complications. However, most of the patients are delighted with the results.
It is important to bear in mind that artificial knee does not feel or function like normal knee. It will feel different. Also results are not as favourable in patients under age of 60. Don’t compare two knees even if you had one replaced earlier!
Possible complications specific to knee replacement include numbness on the side of knee, residual pain in front of kneecap, failure and damage to nerve and vessel. Other complications include a small risk of clot in leg (DVT) or clot breaking loose (PE), pain, swelling, bleeding, revision surgery in case of wear or failure.
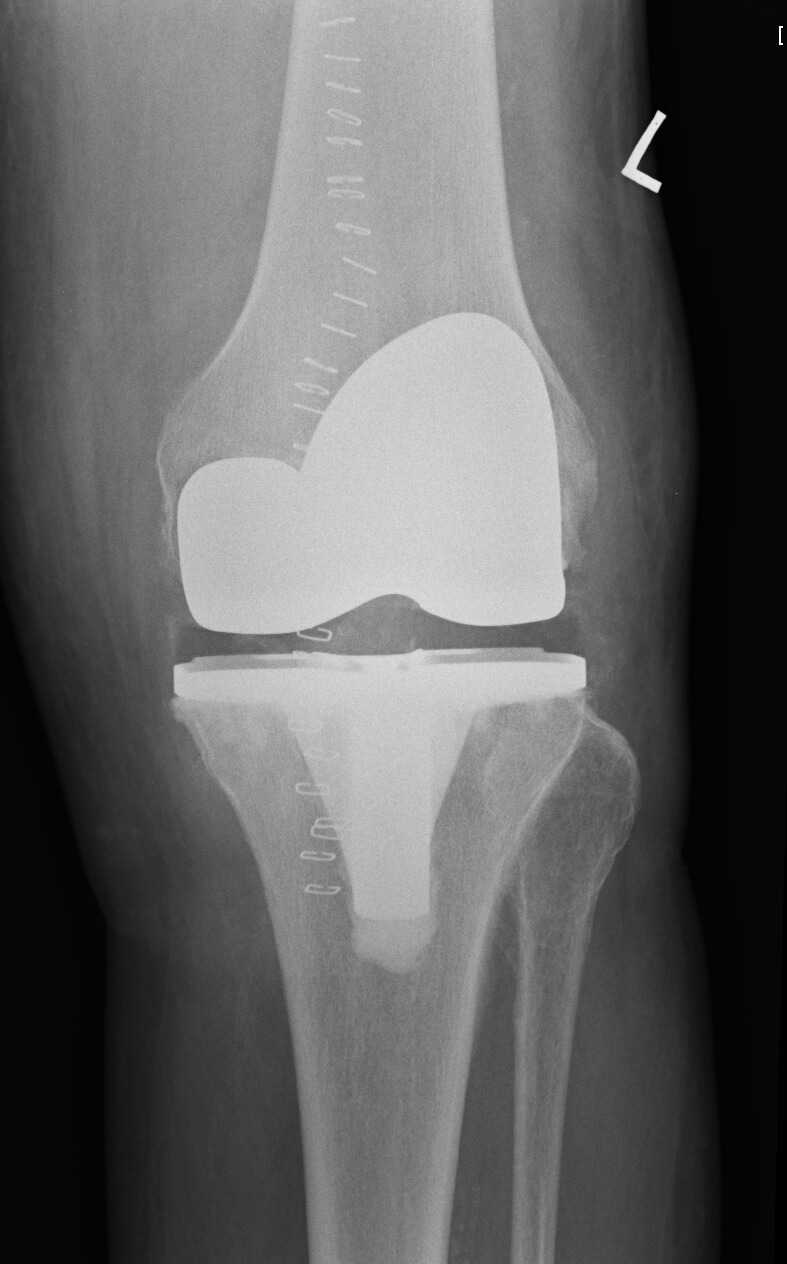
Which knee replacement do you use?
My preferred choice is Nexgen knee replacement. It has excellent track record. I have used it since 2007 at Warrington and Spire.
WHAT IS THE RECOVERY?
You will have big padded dressing after operation and a cryocuff (cold ice compression). You will be given exercises to keep foot, ankle and calf muscles working. You will also be taught knee bending and exercise to strengthen quads (to straighten knee). It is important to try and get knee straight, bend will improve. Walking is possible soon after the operation. A physio will guide you regarding your progress.
You will have would check and removal of clips two weeks after operation. I will review you six weeks after the operation. You can walk as far as you are able to once comfortable.
It may be preferable to use a stick or hiking pole for long distances. Use shower for the first six weeks instead of a bath. You may resume swimming, dancing and light gym work (bike and cross trainer) after 6 weeks. You can return to sedentary office job after 6 to 8 weeks. If you have heavy job, you may return back to work in about three months with some alteration in duties.
